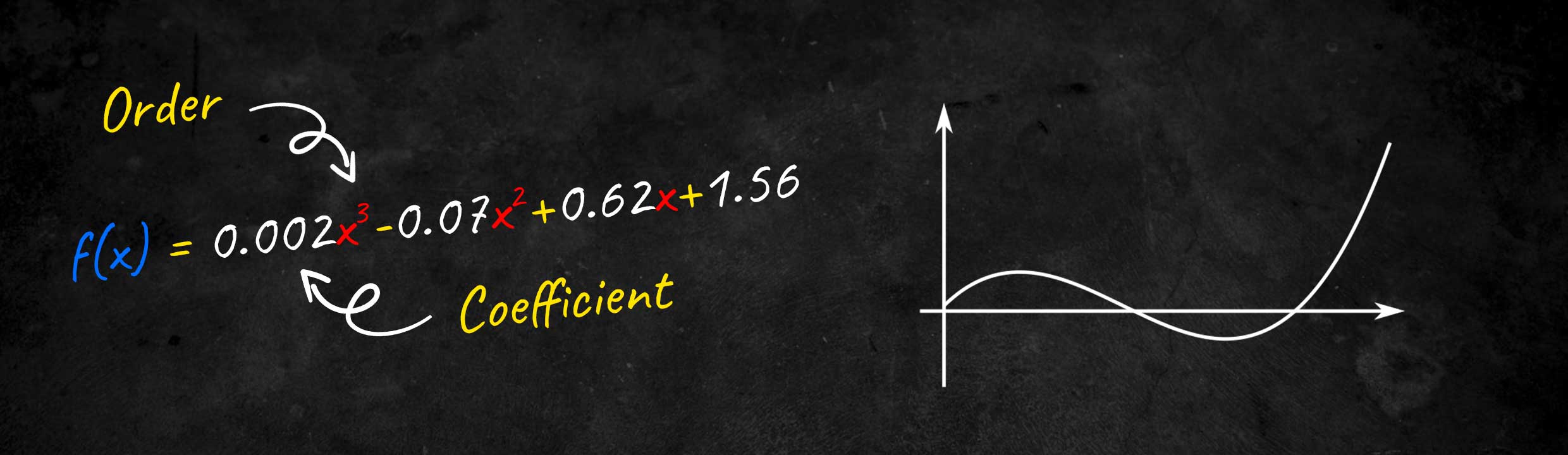Calculating the coefficients of a polynomial equation can be done using matrices, specifically through matrix inversion. In this topic, we will discuss how to use matrices to find the coefficients of a polynomial equation and the steps involved in this process.
You can watch this video where I talked about this subject as well as introducing a C library for calculating coefficients of a Polynomial equation.
A polynomial equation is an equation that contains one or more terms in which the variables are raised to positive integer powers. For example, the equation y = ax2 + bx + c is a polynomial equation of degree two. The coefficients in this equation are a, b, and c. These coefficients are constants that determine the shape and position of the graph of the polynomial equation.
f(x) = ax3+ bx2+ cx+d
a, b, c, and d are the coefficients
To calculate the coefficients of a polynomial equation, we need to have a system of equations that represent the values of the coefficients. We can then use matrices to solve this system of equations and find the values of the coefficients.
The first step in this process is to set up the system of equations. We do this by taking several values of x and calculating the corresponding values of y. For example, if we take x = 1, 2, and 3, we can calculate the values of y for each of these values of x. This will give us three equations that we can use to find the coefficients of the polynomial equation.
a0 + a1x0 + a2x02 + a3x03 + … + anx0n = y0
a0 + a1x1 + a2x12 + a3x13 + … + anx1n = y1
.
.
.
a0 + a1xn + a2xn2 + a3xn3 + … + anxnn = yn
Once we have the system of equations, we can represent it in matrix form. We do this by creating a matrix A that contains the coefficients of the variables, a matrix X that contains the values of the variables, and a matrix B that contains the values of y. We can then write the equation as AX = B.
| 1 x0 x02 x03 … x0n | | a0 | = | y0 |
| 1 x1 x12 x13 … x1n | | a1 | = | y1 |
| . . . . . | | . | = | . |
| . . . . . | | . | = | . |
| . . . . . | | . | = | . |
| 1 xn xn2 xn3 … xnn | | an | = | yn |
where the first column of the matrix represents the coefficients a0, a1, a2, …, an, the second column represents x0, x1, x2, …, xn raised to the power of 1, the third column represents x0^2, x1^2, x2^2, …, xn^2 raised to the power of 1, and so on. The last column represents the values of y0, y1, y2, …, yn.
To find the values of X, we need to invert matrix A. This can be done using a matrix calculator or the Gauss-Jordan elimination method. Once we have the inverted matrix A, we can multiply both sides of the equation by the inverse of A. This will give us X = A^-1B, which represents the values of the coefficients of the polynomial equation.
In summary, calculating the coefficients of a polynomial equation using matrices involves setting up a system of equations, representing it in matrix form, inverting matrix A, and multiplying the inverse of A by matrix B to find the values of the coefficients. This process can be used for polynomial equations of any degree and can be useful in solving complex equations.